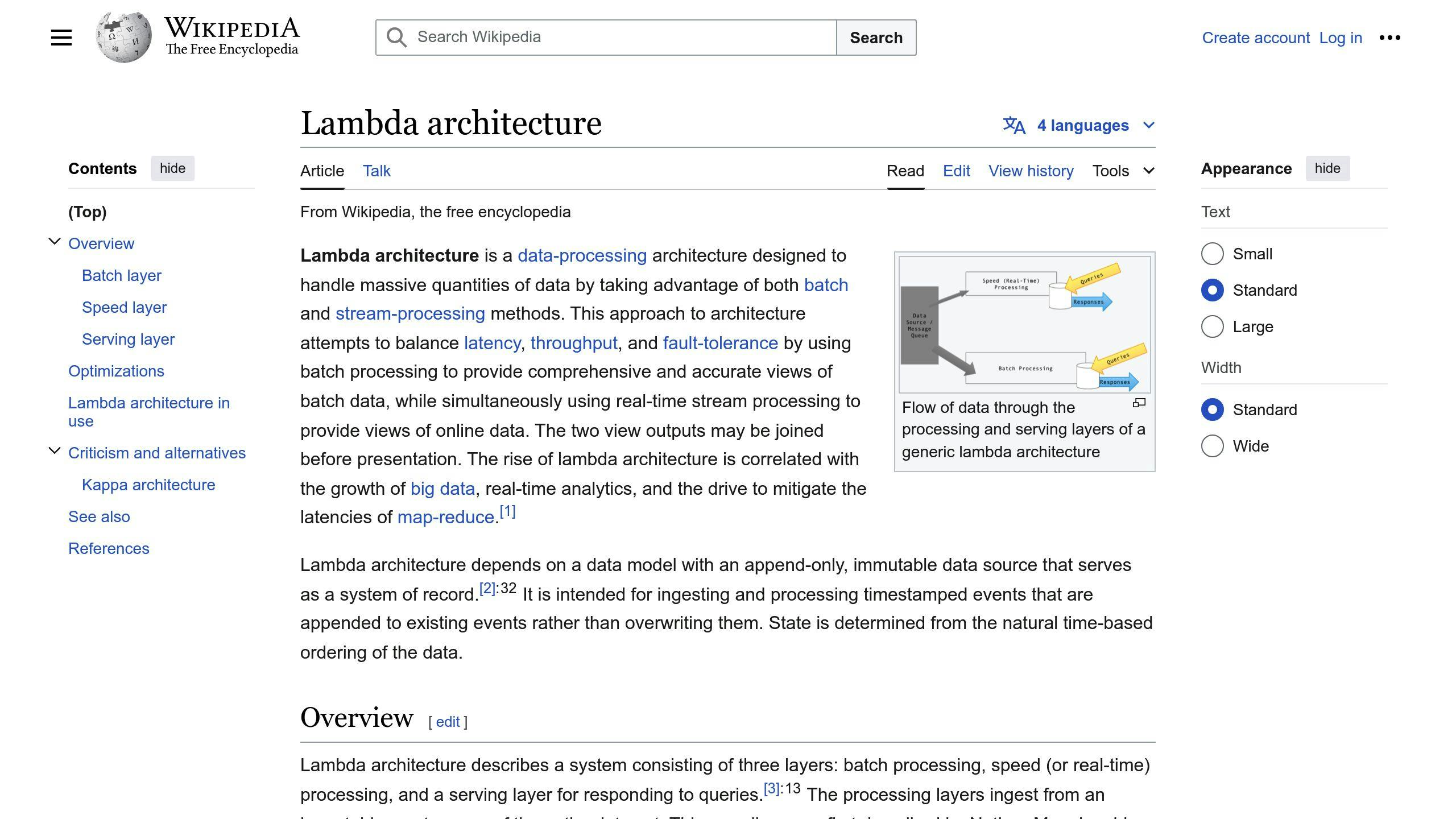
Lambda Architecture is a framework for processing large amounts of data that combines batch and real-time processing. Here's what you need to know:
-
Three main layers:
- Batch layer: Processes large amounts of historical data
- Speed layer: Handles real-time data processing
- Serving layer: Makes processed data available for queries
-
Key principles:
- Data is immutable
- Uses both recomputation and incremental processing
- Tasks are divided among layers
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Scalable | Handles large data volumes |
| Fault-tolerant | Continues working if parts fail |
| Real-time processing | Enables quick responses |
| Unified view | Simplifies data analysis |
Lambda Architecture helps companies process and use big data more effectively, but it can be complex to set up and maintain. It's best suited for organizations with large amounts of historical data and real-time processing needs.
Related video from YouTube
2. Big Data Challenges
2.1 The Three Vs of Big Data
Big data has three main features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Volume | Large amounts of data from many sources |
| Velocity | How fast data is made and processed |
| Variety | Different types of data (structured, semi-structured, unstructured) |
In 2024, there's more data than ever. This creates new problems:
- Need for more trained workers
- Keeping data sources in sync
- Lack of good data management
- Risk of data breaches
2.2 Real-Time Processing Needs
Real-time processing is important for quick business decisions. It helps companies react fast to changes.
Challenges of real-time processing:
- Must be quick
- Must handle lots of data
- Must be accurate
2.3 Problems with Batch Processing
Batch processing deals with large amounts of data at once, often offline. It has some drawbacks:
| Problem | Impact |
|---|---|
| Slow | Delayed insights and decisions |
| Not flexible | Hard to change for new needs |
| Resource-heavy | Uses a lot of storage, computing power, and people |
These issues can make batch processing costly and time-consuming.
3. Key Principles of Lambda Architecture
Lambda Architecture uses three main ideas to handle big data well. These ideas help the system work quickly and correctly.
3.1 Data Doesn't Change
In Lambda Architecture, once data is added, it can't be changed or removed. This keeps the data correct and helps make good choices. New data is added to the end, not mixed with old data. This way, the system can handle lots of data without mistakes.
3.2 Two Ways to Process Data
Lambda Architecture uses two ways to handle data:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Recomputation | Processes all data again when new data comes in |
| Incremental | Only processes new data and updates results |
The system uses both ways:
- Batch layer: Uses recomputation for large amounts of data
- Speed layer: Uses incremental processing for real-time data
3.3 Splitting Tasks
Lambda Architecture splits tasks into different parts:
| Layer | Job |
|---|---|
| Batch | Handles large amounts of data |
| Speed | Processes real-time data |
| Serving | Shows data to users |
4. Three Layers of Lambda Architecture
Lambda Architecture has three main parts that work together to handle big data quickly and reliably. Each part does a different job to make sure the system can process lots of data well.
4.1 Batch Layer
The batch layer handles large amounts of old data in groups. It:
- Processes all data, both old and new
- Gives a full, correct view of the data
- Works slowly but accurately
- Can be run again without changing the result
This layer provides a solid base for comparing with real-time data.
4.2 Speed Layer (Stream Processing)
The speed layer deals with new data as it comes in. It:
- Processes data streams quickly
- Handles data from things like IoT devices, social media, or money transfers
- Gives quick answers to questions
- Helps make fast decisions
This layer allows for quick responses to new information.
4.3 Serving Layer
The serving layer combines the work of the batch and speed layers. It:
- Gets results from both the batch and speed layers
- Puts all the data together in one place
- Lets users look at the data
- Only allows reading data, not changing it
This layer makes it easy for users to see all the processed data in one spot.
| Layer | Main Job | Speed | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch | Process old data | Slow | High |
| Speed | Handle new data | Fast | Medium |
| Serving | Show combined data | Medium | High |
5. How to Implement Lambda Architecture
Setting up Lambda Architecture requires careful planning and execution. Here's how to get started:
5.1 Choosing Tools
Pick the right tools for each part of Lambda Architecture:
| Layer | Recommended Tools |
|---|---|
| Batch | Apache Hadoop |
| Speed | Apache Spark |
| Data Streaming | Apache Kafka |
| Real-time Views | Apache Cassandra |
| Serving | Apache HBASE |
5.2 Important Design Points
When creating your Lambda Architecture, think about:
- Where your data comes from
- How much data you need to process and how fast
- How users will look at the data
- Which tools work best for your needs
5.3 Making the System Work Well
To keep your Lambda Architecture running smoothly:
| Aspect | Action |
|---|---|
| Growth | Make sure the system can handle more data |
| Reliability | Plan for problems and how to fix them |
| Upkeep | Check the system often and fix issues |
6. Advantages of Lambda Architecture
Lambda Architecture offers several benefits for big data processing. Here are the main advantages:
6.1 Mixing Real-Time and Batch Processing
Lambda Architecture handles both batch and real-time processing well. This allows systems to:
| Processing Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Batch | Handle large amounts of data at set times |
| Real-time | Give quick insights into new data |
The batch layer works with old data, while the speed layer deals with new data. This setup helps systems handle different workloads well.
6.2 System Reliability and Data Accuracy
Lambda Architecture is built to keep working even if parts of it fail. It does this by:
- Storing all data in the batch layer
- Keeping data correct and consistent
- Allowing re-runs of indexing jobs if needed
- Letting the speed layer keep indexing new data during problems
This design helps make sure the system stays up and running, and the data stays accurate.
6.3 Adjusting to New Needs
Lambda Architecture is easy to change. It lets companies:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Use different tools | Process data in various ways |
| Change quickly | Meet new business needs |
| Handle more data | Grow as data amounts increase |
This flexibility helps companies keep up with changing needs and growing data volumes.
sbb-itb-9890dba
7. Drawbacks and Limits
7.1 Hard to Set Up
Setting up Lambda Architecture can be tough, especially for those new to batch and stream processing. It needs:
- Deep knowledge of the tools used
- Lots of time and resources
This can make it hard for some companies to use.
7.2 Needs Constant Care
Keeping Lambda Architecture running well takes work:
| Task | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Check batch layer | Make sure it processes data correctly |
| Monitor speed layer | Ensure real-time data is handled well |
| Keep layers in sync | Avoid data mismatches |
Companies with few resources or experts may find this hard.
7.3 Data Mismatch Issues
Lambda Architecture can have problems with data matching up:
- Batch and speed layers may show different results
- This can lead to wrong information
- Fixing these issues takes time and effort
| Layer | Data Processing | Potential Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Batch | Processes old data | May not have latest updates |
| Speed | Handles new data | Might miss some data in processing |
These problems can make the system less trustworthy.
While Lambda Architecture has good points, it's important to know its weak spots. Understanding these helps companies plan better when using this system.
8. Lambda vs. Other Approaches
8.1 Lambda vs. Kappa Architecture
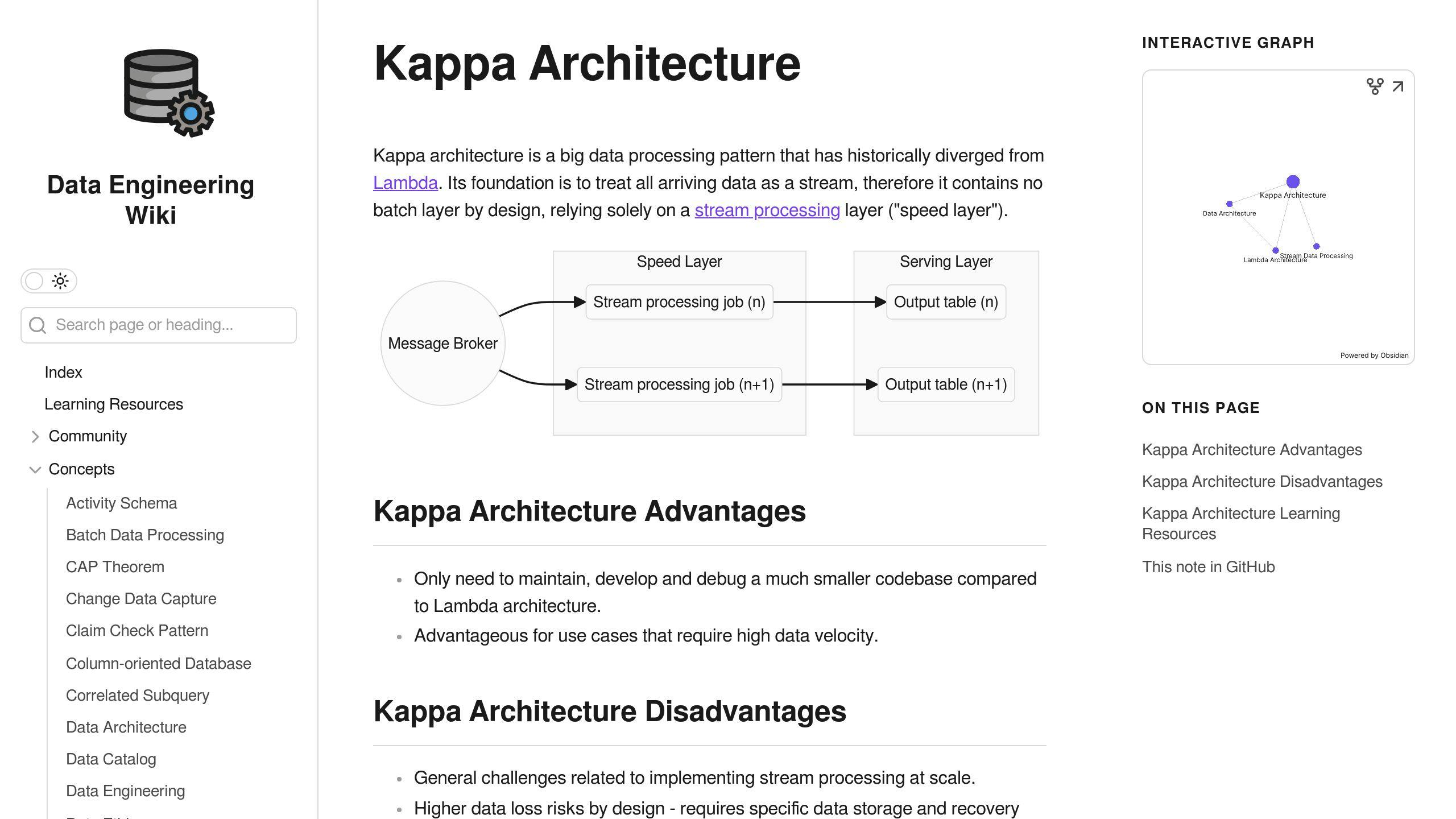
Lambda and Kappa are two ways to handle big data. Here's how they differ:
| Feature | Lambda Architecture | Kappa Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Uses batch and speed layers | Uses single stream processing |
| Data handling | Separate historical and real-time | All data as a stream |
| Strengths | Good for large historical data | Simpler to set up and run |
| Weaknesses | Can be complex | May not suit all needs |
Lambda is good for big companies with lots of old data. Kappa works well for smaller setups that need quick results.
8.2 Mixed Approaches
Some companies mix Lambda and Kappa. This can give the best of both, but it can also make things more complex.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Handles old and new data well | More complex to set up |
| Gives quick insights | Needs more resources |
| Works with different data types | Can be hard to manage |
8.3 When to Use Lambda Architecture
Lambda works best for:
- Big amounts of old data
- Needing exact results quickly
- Real-time reports
- Working with many data sources
It's not great for:
- Simple, cheap setups
- Only real-time data needs
- Small amounts of data
9. Tips for Using Lambda Architecture
9.1 How to Model Data
When using Lambda Architecture, it's important to model your data well. Here are some tips:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Know what you need | Figure out what data you want to process and what you want to learn from it |
| Use a model that can grow | Pick a data model that can handle lots of data as your system gets bigger |
| Keep data the same everywhere | Make sure your data stays the same across all parts of the Lambda Architecture |
9.2 Making the System Faster
To speed up your Lambda Architecture system, try these tips:
| Tip | How it helps |
|---|---|
| Make the speed layer better | Improve how the speed layer handles data quickly |
| Use caching | Store some data for quick access to make the system respond faster |
| Spread out the work | Use multiple computers to do the work, so it gets done faster |
9.3 Finding and Fixing Problems
To keep your Lambda Architecture system working well, check for issues often and fix them quickly. Here's how:
| What to do | Why it's important |
|---|---|
| Watch how the system is working | Find slow parts or problems early |
| Use tools to find errors | Find and fix issues quickly with special software |
| Check your data regularly | Make sure the data is correct and matches across the system |
10. What's Next for Lambda Architecture
10.1 New Big Data Processing Trends
Big data processing is always changing. Lambda Architecture is changing too. Here are some new trends:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud-based systems | Help handle more data and work better |
| Real-time processing | Deal with data as it comes in |
These trends are helping Lambda Architecture work better with big data.
10.2 Possible Upgrades and New Ideas
People are working on making Lambda Architecture better:
| Upgrade | How it helps |
|---|---|
| Machine learning | Makes the system work faster and handle more data |
| New uses | Using Lambda for things like Internet of Things (IoT) data |
These changes could help Lambda Architecture do more and work better.
10.3 Working with AI and Machine Learning
Mixing AI and machine learning with Lambda Architecture can help a lot:
| Benefit | Example |
|---|---|
| Find new information | AI can spot odd patterns in data quickly |
| Work faster | Machine learning can help the speed layer do its job better |
11. Wrap-Up
11.1 Key Takeaways
This guide has covered the basics of Lambda Architecture, its parts, and how it's used in big data processing. We've looked at:
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Big data challenges | Volume, speed, and types of data |
| Real-time processing | Quick data handling for fast decisions |
| Lambda Architecture | How it mixes batch and real-time processing |
We've also explained the main ideas behind Lambda Architecture:
- Data doesn't change once added
- Two ways to process data: all at once or bit by bit
- Splitting tasks into different parts
11.2 Lambda Architecture's Role Today
Lambda Architecture is a strong choice for handling lots of data in today's systems. It's good because:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Balances speed and accuracy | Gives quick insights without losing data quality |
| Handles different data loads | Works well with both old and new data |
| Keeps working if parts fail | Helps keep data safe and available |
As data keeps growing, Lambda Architecture will likely become more important. By understanding how it works, companies can use their data better and make smarter choices quickly.
FAQs
What are the uses of Lambda Architecture?
Lambda Architecture helps with big data processing in different ways:
| Use Case | Batch Layer | Speed Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Fraud Detection | Looks at old transaction data | Checks new transactions quickly |
| IoT Data Processing | Studies past sensor data | Handles new data from devices right away |
What are the limitations of Lambda Architecture?
Lambda Architecture has some drawbacks:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Hard to set up | Needs two separate systems for batch and streaming |
| Can be costly | Running two systems may cost more at first |
| Data matching issues | Keeping data the same in both parts can be tricky |
These issues can make it hard for some companies to use Lambda Architecture well.



